1. β-シクロデキストリン(βCD)って何?
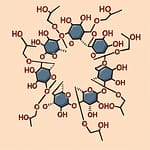
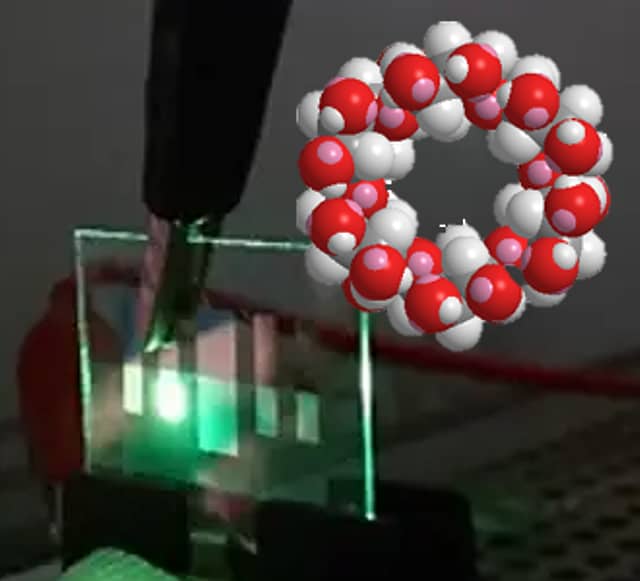
β-シクロデキストリン(βCD)は、ドーナツ形の“糖の輪”のような分子です。外側は水になじみやすく、内側は油(疎水性)に近い性質を持つため、内側の空間に香り成分・薬・農薬・色素などを「包み込む(包接する)」ことができます。
その結果、
- 水に溶けにくい物質を溶けやすくする
- 光・pH・酸化還元などに応じてゆっくり放出する
- 不安定な物質を守る(安定化)する
- 材料の孔(あな)作りや表面機能化に使って高機能材料を作る
…といった応用が可能になります。
Paper 1:糖尿病創傷の治癒を促す“スマート創傷ドレッシング”
- Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal
- Title: pH-triggered hierarchical responsive release of RVT by HP-beta-CD nanoparticles loaded hydrogel dressing to promote diabetic wound healing
- ポイント(一般向け):
糖尿病の傷は治りにくいことがあります。この研究では、傷の環境(pH)に合わせて薬(RVT:レスベラトロール)を必要なタイミングで放出できるハイドロゲル(柔らかいゲル状素材)を提案しています。
βCDの誘導体(HP-βCD)で薬を包み、ゲルの中に入れることで「溶けにくい薬を扱いやすくし、狙った場所で効かせる」設計になっています。 - βCDの役割:薬(RVT)の包接 → 溶解性・安定性の改善、放出制御の土台
Paper 2:農薬を“狙って効かせる”二重応答マイクロキャリア
- Journal: Small
- Title: Dual-responsive diatomite microcarriers enhance targeted delivery of emamectin benzoate to Plutella xylostella
- ポイント(一般向け):
害虫(コナガ:Plutella xylostella)に効く農薬(エマメクチン安息香酸塩)を、必要なところで効率よく届ける研究です。
“二重応答(dual-responsive)”という設計で、環境条件に応じて放出をコントロールし、農薬を無駄にしにくい(=環境負荷を下げやすい)方向を目指しています。 - βCDの役割:農薬分子の包接や担持設計の一部として、放出制御・安定化に寄与(文献リスト中のキーワードにβCDが含まれます)
Paper 3:電池材料づくりにβCDを活用(高性能な多孔質炭素)
- Journal: Journal of Energy Storage
- Title: Dual-activation with oyster shell: Synergistic engineering of N/P co-doped hierarchical porous carbon from intumescent flame retardants for high-performance dual-ion batteries
- ポイント(一般向け):
電池の性能を上げるには、電極材料の「表面積」や「イオンが通りやすい孔構造」が重要です。
この研究では、貝殻(オイスターシェル)と、難燃剤系の原料(βCD、APP、メラミン)を混ぜて炭化し、窒素(N)・リン(P)を入れた多孔質炭素を作っています。材料内部の孔が増え、さらにN/Pの化学状態も最適化され、電池性能向上につながる設計です。 - βCDの役割:炭素源・構造形成に関与 → 多孔質化、ヘテロ原子導入設計の一部
3. まとめ
βCDは「分子を包み込む」機能を中心に、医療(創傷治癒)、農業(農薬デリバリー)、エネルギー(電池材料)まで幅広く使われています。
共通する狙いは、“必要なものを、必要な場所へ、必要なタイミングで”届けたり、材料の構造を賢く設計することです。
English (EN)
What is β-cyclodextrin (βCD)?
β-cyclodextrin (βCD) is a donut-shaped cyclic sugar molecule. Its outer surface is hydrophilic (water-friendly), while its inner cavity is relatively hydrophobic (oil-like).
This unique structure allows βCD to encapsulate (“host–guest inclusion”) various molecules such as drugs, fragrances, pesticides, and dyes.
As a result, βCD can:
– Improve apparent solubility of poorly soluble molecules
– Provide controlled / triggered release (e.g., pH-responsive systems)
– Enhance stability by shielding guest molecules
– Serve as a building block/precursor in functional materials (porous carbons, surface modification, etc.)
Paper 1 : Smart hydrogel dressing for diabetic wound healing
- Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal (IF 13.2)
- Title: pH-triggered hierarchical responsive release of RVT by HP-beta-CD nanoparticles loaded hydrogel dressing to promote diabetic wound healing
- Plain-language takeaway:
Diabetic wounds often heal slowly. This work proposes a hydrogel dressing that releases resveratrol (RVT) in response to wound pH, aiming to deliver the active compound when and where it is most needed. - Role of βCD: HP-βCD forms inclusion complexes with RVT → improved solubility/stability and a basis for controlled release
Paper 2 : Dual-responsive microcarriers for targeted pesticide delivery
- Journal: Small (IF 12.1)
- Title: Dual-responsive diatomite microcarriers enhance targeted delivery of emamectin benzoate to Plutella xylostella
- Plain-language takeaway:
This study designs microcarriers that can deliver a pesticide more effectively to the pest insect Plutella xylostella, potentially reducing waste and environmental burden through controlled/targeted release. - Role of βCD: βCD-related host–guest concepts are used in the material design to support loading/stabilization and release control (βCD appears as a key term in the provided record)
Paper 3 : Using βCD as a precursor for porous carbon in batteries
- Journal: Journal of Energy Storage (IF 9.8)
- Title: Dual-activation with oyster shell: Synergistic engineering of N/P co-doped hierarchical porous carbon from intumescent flame retardants for high-performance dual-ion batteries
- Plain-language takeaway:
Battery electrodes benefit from high surface area and well-connected pores. Here, oyster shell powder and intumescent flame retardants (βCD, ammonium polyphosphate, melamine) are carbonized to create N/P co-doped hierarchical porous carbon, enabling improved battery performance. - Role of βCD: carbon source / structure-forming component contributing to porosity and heteroatom-doping strategies
References
- Chemical Engineering Journal (2026). pH-triggered hierarchical responsive release of RVT by HP-beta-CD nanoparticles loaded hydrogel dressing to promote diabetic wound healing. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2026.172650
- Small (2026). Dual-responsive diatomite microcarriers enhance targeted delivery of emamectin benzoate to Plutella xylostella. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202513220
- Journal of Energy Storage (2026). Dual-activation with oyster shell: Synergistic engineering of N/P co-doped hierarchical porous carbon from intumescent flame retardants for high-performance dual-ion batteries. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2026.114446