[“βCDP”, “β-cyclodextrin”, “cyclodextrin polymer”, “host–guest”, “adsorption”, “drug delivery”, “materials”]
1分でわかる:βCDPは「分子をつかまえる力」を材料にしたもの
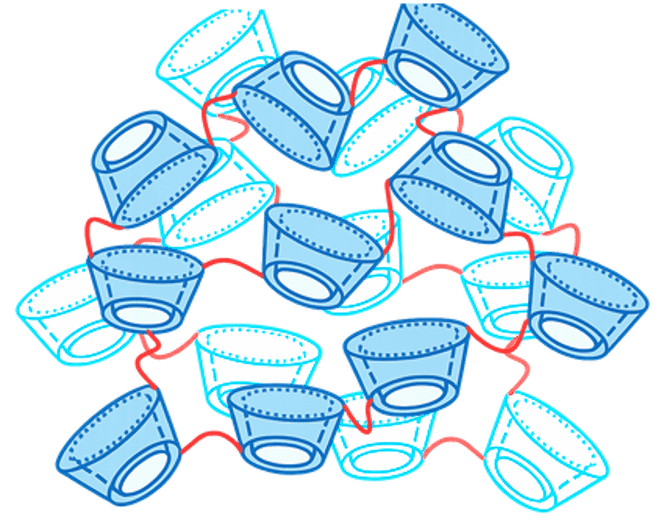
β-シクロデキストリン(βCD)は、ドーナツ状の“空洞”をもつ分子で、条件が合うと別の分子を取り込み(包接)ます。
βCDを多数つないだ βCDポリマー(βCDP) は、空洞が増えることで、
– 不要な分子を捕まえる(吸着・除去)
– 必要な分子を保持し、放出を調整する(ドラッグデリバリー/製剤)
– 分子の動き方を制御する(複合材料・膜・ゲル)
といった応用が期待されます。
このページでは、添付の βCDP_Frontier.txt に含まれる論文から、βCDP/βCD材料の“今どきの使い方”が見える3本を選び、一般の方向けにやさしく解説します。
今回の3本で見える「βCDPの使われ方」
- 医療(神経疾患モデル):コレステロールの“たまり”にアプローチ
- 環境・センシング:色素分子をモデルに、包接×吸着×分光で機能を設計
- 製剤(口腔内フィルム):難溶性薬をβCD複合体として使いこなす
論文ハイライト(3本)
Paper 1: A water-soluble β-cyclodextrin polymer reduces cholesterol accumulation and autophagy dysfunction in vitro and in Niemann-Pick type C disease model mice
- 掲載誌:Carbohydrate Polymers(2026)
- 要点(かんたん解説):
- 水溶性のβ-シクロデキストリンポリマー(βCDP)を用い、細胞・動物モデルでコレステロール蓄積の低減を評価。
- 血中での滞留(循環)時間が長いこと、オートファジー関連の異常が改善する方向の結果を報告。
- 神経変性疾患関連の“分子を捕まえる”材料としての可能性を示す。
- 原文アブストラクト(要約):Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are characterised by cognitive dysfunction and neurological impairment. In both diseases, the abnormal accumulation and disruption of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain may contribute to the…
- DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124676
Paper 2: Supramolecular interactions and adsorption behavior of β-cyclodextrin-functionalized polyacrylates toward Rhodamine B
- 掲載誌:Surfaces And Interfaces(2026)
- 要点(かんたん解説):
- βCD誘導体をポリアクリレートに導入し、色素分子(ローダミンB)などをモデルに包接・吸着挙動を解析。
- UV-Vis/蛍光/誘起円二色性(ICD)/EPRなど複数手法でホスト–ゲスト相互作用を示す。
- 吸着容量や速度論(擬一次モデル、ラングミュア等温線)などを整理し、環境・センシング材料への応用可能性を示す。
- 原文アブストラクト(要約):This study develops novel polymers by functionalizing sodium polyacrylate (NaPA) with beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) derivatives. Successful grafting was confirmed by FTIR and H-1 NMR spectroscopy, while mu DSC analysis revealed that CD units hinder polymer…
- DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2025.108334
Paper 3: Exploring new buccal films based on hydroxyethyl cellulose and Linecaps® combination for the pediatric delivery of hydrophobic molecules
- 掲載誌:Carbohydrate Polymers(2026)
- 要点(かんたん解説):
- βCD誘導体をポリアクリレートに導入し、色素分子(ローダミンB)などをモデルに包接・吸着挙動を解析。
- UV-Vis/蛍光/誘起円二色性(ICD)/EPRなど複数手法でホスト–ゲスト相互作用を示す。
- 吸着容量や速度論(擬一次モデル、ラングミュア等温線)などを整理し、環境・センシング材料への応用可能性を示す。
- 原文アブストラクト(要約):Polysaccharides and starch derivatives can play a role in the development of buccal films and patches. Buccal films are a valid approach to the transmucosal administration of drugs. These drug-delivery systems are adaptable to the mucosal surface, while being…
- DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124499
3本からの共通メッセージ(研究・教育の観点)
- βCDPの価値は「分子レベルの相互作用(包接・結合)」を「材料として使える形(ポリマー、フィルム、機能化高分子)」へ変換できる点にあります。
- “何を捕まえるか(ターゲット分子)”と、“どう使うか(医療/環境/製剤)”で、設計すべき材料パラメータが変わるのがポイントです。
- 水溶性、循環時間、細胞毒性(医療)
- 吸着容量、速度論、分光応答(環境・センシング)
- 味・放出・粘膜付着・機械強度(製剤)
用語ミニ解説
- 包接(ホスト–ゲスト):βCD(ホスト)の空洞にゲスト分子が入る現象。
- 誘起円二色性(ICD):分子が空洞に入り“向き”が揃うと、円偏光に対する吸収差が現れることがある指標。
- EPR(電子スピン共鳴):ラジカル(スピンプローブ)の運動性変化から、結合や拘束を読み取る手法。
- ラングミュア等温線:吸着が単分子層で進むような場合の代表的な吸着モデル。
参考文献(添付ファイル収録論文から)
- Kubohira, Y, Okano, N, Taharabaru, T, Ishimatsu, A, Era, T, Yanagihara, K, Ishikura, K, Nakagawa, Y, Higashi, T, Motoyama, K. A water-soluble β-cyclodextrin polymer reduces cholesterol accumulation and autophagy dysfunction in vitro and in Niemann-Pick type C disease model mice. Carbohydrate Polymers (2026) 374, Article 124676. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124676.
- Leonties, AR, Baran, A, Ionita, G, Precupas, A, Sanda, G, Ciutu, ML, Bucur, AG, Jerca, VV, Aricov, L. Supramolecular interactions and adsorption behavior of β-cyclodextrin-functionalized polyacrylates toward Rhodamine B. Surfaces And Interfaces (2026) 80, Article 108334. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2025.108334.
- Magnano, GC, Scomparin, A, Argenziano, M, Spagnolo, R, Muntoni, E, Voinovich, D, Hasa, D, Bianchi, V, De Munari, I, Cavalli, R. Exploring new buccal films based on hydroxyethyl cellulose and Linecaps® combination for the pediatric delivery of hydrophobic molecules. Carbohydrate Polymers (2026) 371, Article 124499. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124499.
English (for website)
In one minute: βCDP turns “molecule-capturing” into a practical material
β-Cyclodextrin (βCD) is a donut-shaped host molecule with a cavity that can include guest molecules under suitable conditions.
A βCD polymer (βCDP) connects many βCD units, increasing available cavities and enabling:
– capture/removal of target molecules (adsorption)
– retention and controlled release (drug delivery/formulation)
– control of transport and interfaces in composites/films
Below are three recent papers selected from the attached file βCDP_Frontier.txt, summarized in plain language.
What these 3 papers collectively show
- Biomedical direction: βCDP for cholesterol-related dysfunction in disease models
- Environmental/sensing direction: βCD-functionalized polymers controlling binding/adsorption and optical response
- Formulation direction: βCD complexes enabling practical dosage forms (e.g., buccal films)
Highlights (3 papers)
Paper 1: A water-soluble β-cyclodextrin polymer reduces cholesterol accumulation and autophagy dysfunction in vitro and in Niemann-Pick type C disease model mice
- Journal: Carbohydrate Polymers (2026)
- Key takeaways (plain language):
- Evaluates a water-soluble β-cyclodextrin polymer (βCDP) in cell and mouse models with cholesterol accumulation.
- Reports longer circulation time and improvements linked to cholesterol reduction and autophagy-related dysfunction.
- Positions βCDP as a potential therapeutic “molecule-capturing” material in neurodegeneration-related contexts.
- Abstract (condensed): Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are characterised by cognitive dysfunction and neurological impairment. In both diseases, the abnormal accumulation and disruption of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain may contribute to the…
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124676
Paper 2: Supramolecular interactions and adsorption behavior of β-cyclodextrin-functionalized polyacrylates toward Rhodamine B
- Journal: Surfaces And Interfaces (2026)
- Key takeaways (plain language):
- Grafts βCD derivatives onto polyacrylates and probes host–guest binding/adsorption using Rhodamine B and spin probes.
- Supports inclusion/interaction via UV–Vis, fluorescence, induced circular dichroism (ICD), and EPR.
- Quantifies adsorption capacity and kinetics (pseudo-first-order, Langmuir), highlighting potential for environmental and smart sensing materials.
- Abstract (condensed): This study develops novel polymers by functionalizing sodium polyacrylate (NaPA) with beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) derivatives. Successful grafting was confirmed by FTIR and H-1 NMR spectroscopy, while mu DSC analysis revealed that CD units hinder polymer…
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2025.108334
Paper 3: Exploring new buccal films based on hydroxyethyl cellulose and Linecaps® combination for the pediatric delivery of hydrophobic molecules
- Journal: Carbohydrate Polymers (2026)
- Key takeaways (plain language):
- Grafts βCD derivatives onto polyacrylates and probes host–guest binding/adsorption using Rhodamine B and spin probes.
- Supports inclusion/interaction via UV–Vis, fluorescence, induced circular dichroism (ICD), and EPR.
- Quantifies adsorption capacity and kinetics (pseudo-first-order, Langmuir), highlighting potential for environmental and smart sensing materials.
- Abstract (condensed): Polysaccharides and starch derivatives can play a role in the development of buccal films and patches. Buccal films are a valid approach to the transmucosal administration of drugs. These drug-delivery systems are adaptable to the mucosal surface, while being…
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124499
Common takeaway
βCDP research links molecular recognition (host–guest inclusion) to macroscopic functions (therapy-oriented materials, adsorption/sensing, and formulation performance).
Design requirements differ by application—solubility and circulation (biomed), adsorption capacity/kinetics and spectroscopic readouts (environment/sensing), or release/mucoadhesion/mechanics (formulation).
References (from the attached file)
- Kubohira, Y, Okano, N, Taharabaru, T, Ishimatsu, A, Era, T, Yanagihara, K, Ishikura, K, Nakagawa, Y, Higashi, T, Motoyama, K. A water-soluble β-cyclodextrin polymer reduces cholesterol accumulation and autophagy dysfunction in vitro and in Niemann-Pick type C disease model mice. Carbohydrate Polymers (2026) 374, Article 124676. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124676.
- Leonties, AR, Baran, A, Ionita, G, Precupas, A, Sanda, G, Ciutu, ML, Bucur, AG, Jerca, VV, Aricov, L. Supramolecular interactions and adsorption behavior of β-cyclodextrin-functionalized polyacrylates toward Rhodamine B. Surfaces And Interfaces (2026) 80, Article 108334. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2025.108334.
- Magnano, GC, Scomparin, A, Argenziano, M, Spagnolo, R, Muntoni, E, Voinovich, D, Hasa, D, Bianchi, V, De Munari, I, Cavalli, R. Exploring new buccal films based on hydroxyethyl cellulose and Linecaps® combination for the pediatric delivery of hydrophobic molecules. Carbohydrate Polymers (2026) 371, Article 124499. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124499.