このページのねらい
このページでは、1 本のレビュー論文(Farfan らによる金属ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトの総説)だけをもとに、
その内容を 「3つのテーマ」に分けて、有機ELに関心のある一般の方にもわかりやすく解説します。
扱う3つのテーマは次のとおりです。
- 金属ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトとは?
- 高分子・バイオポリマー(シクロデキストリンを含む)との複合化
- 光るデバイス(LED・ディスプレイ)への応用と今後の展望
1. 金属ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトとは?
ペロブスカイトって何?
ペロブスカイトとは、もともと鉱物の名前ですが、
材料科学の世界では「特定の結晶構造を持つ化合物」の総称として使われます。
金属ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトは、おおまかに言うと
- 金属イオン(鉛 Pb、スズ Sn、ゲルマニウム Ge など)
- ハロゲン(塩素 Cl、臭素 Br、ヨウ素 I)
- 有機カチオン(メチルアンモニウム MA、ホルムアミジニウム FA など)や無機カチオン(Cs など)
からなる 半導体材料 です。
なぜ注目されているのか?
このレビュー論文によると、金属ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトは次のような特徴を持ちます。
- とてもよく光る(高い発光効率)
- 発光色がシャープで色純度が高い
- 溶液プロセスなど低コストな方法で薄膜化できる
- 電気的な性質も良く、太陽電池・LED・レーザーなど幅広い応用が可能
そのため、ペロブスカイトは
- 太陽電池(高効率で話題になった)
- 白色光源やカラーディスプレイ用 LED
- 光増幅やレーザー
などへ急速に応用研究が広がっています。
2. 高分子・バイオポリマーとの複合化 ― シクロデキストリンの役割
課題:ペロブスカイトは「壊れやすい」
一方で、ペロブスカイト材料は
- 湿気(⾼湿度)
- 酸素
- 熱
- 強い光
に弱く、性能が劣化しやすいという大きな問題があります。
レビュー論文の主眼は、この「弱さ」をどう克服するかにあります。
解決策:高分子・バイオポリマーと混ぜる
論文では、ペロブスカイトを
- 一般的な高分子(PMMA、PVDF など)
- バイオポリマー(デンプン、シクロデキストリン、ポリ乳酸、ポリリシンなど)
と組み合わせて 複合材料(コンポジット) にする研究が多数紹介されています。
このような複合化によって、
- ペロブスカイト粒子の大きさや形を制御できる
- 表面を高分子で「コーティング」して、水や酸素から守る
- フレキシブルなフィルムとして加工しやすくなる
といったメリットが得られます。
シクロデキストリンを含むバイオポリマー
特にこのレビューでは、バイオポリマーの一つとして
- デンプン(starch)
- シクロデキストリン(cyclodextrin)
- ポリ乳酸(PLA)
- ポリリシン
などが例示されています。
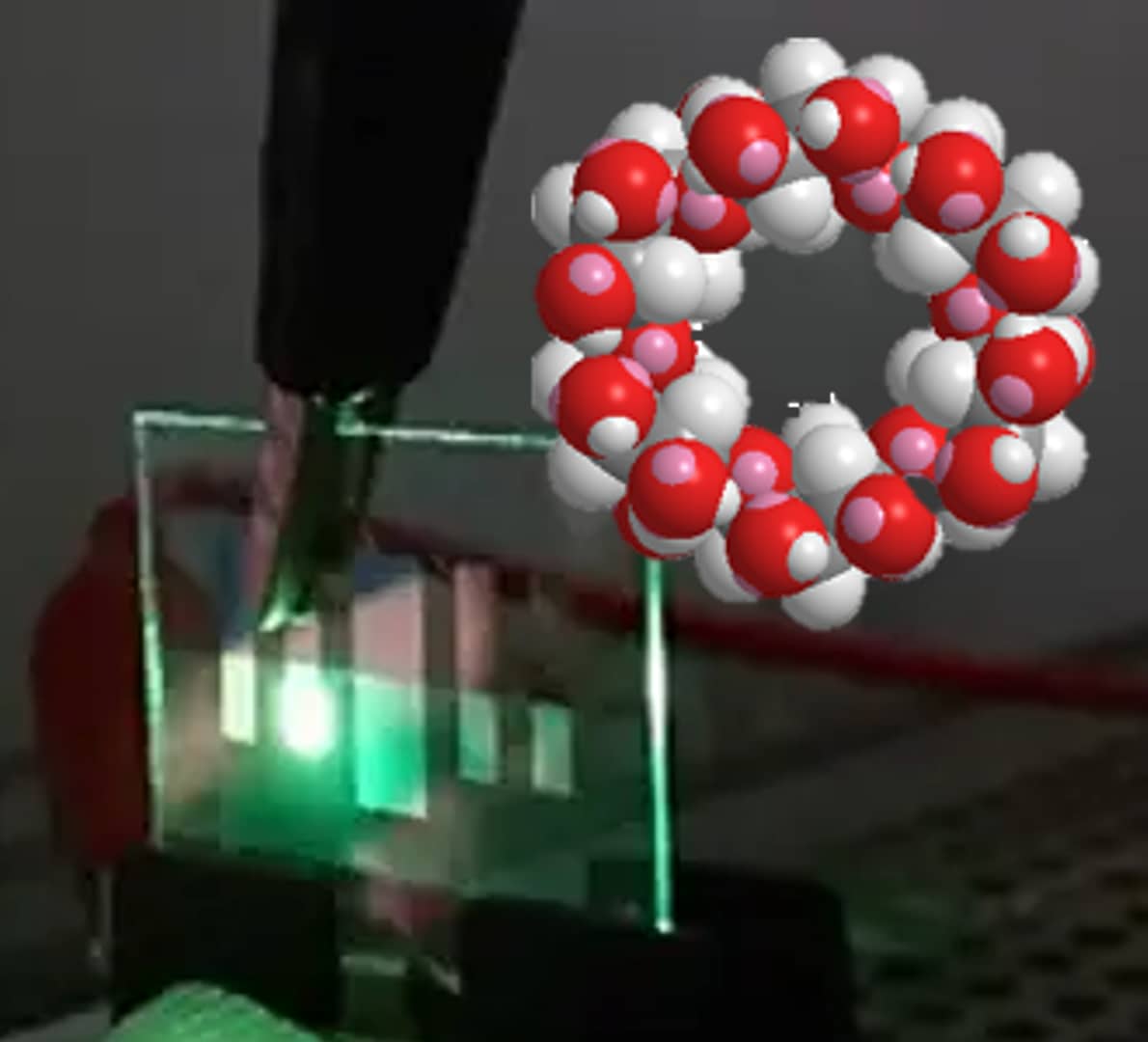
シクロデキストリン(CD)は、デンプンを原料とした環状オリゴ糖で、
- 真ん中に「かご」のような空洞を持ち、
- イオンや小さな有機分子を包み込む(ホスト–ゲスト)
という特徴があります。
この「かご構造」を使ってペロブスカイトの前駆体イオンやナノ結晶の周りを取り囲むことで、
- 結晶成長をコントロールする
- 表面を保護し、湿気や光に対する安定性を高める
といった効果が期待されています。
3. 光るデバイス(LED・ディスプレイ)への応用と展望
ペロブスカイトLED(PeLED)
レビュー論文の中では、金属ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトを用いた
- 高輝度・高色純度の ペロブスカイトLED(PeLED)
- ディスプレイ用バックライトや画素材料
- レーザーやその他の光デバイス
への応用例が幅広く紹介されています。
特に、ペロブスカイトナノ結晶を高分子・バイオポリマー中に分散させた複合膜は、
- 光がよく出やすい
- 安定性が高い
- 大面積コーティングしやすい
という理由から、次世代の照明・ディスプレイ材料として期待されています。
有機ELとの関係
ペロブスカイトは「無機」に近い材料ですが、デバイス構造や課題は有機ELと共通する点が多くあります。
- 「よく光る」だけでなく、「長持ちする」ことが重要
- 電極との界面やエネルギー準位の整合がカギ
- フレキシブル基板上に塗布・印刷で作りたい
など、デバイス全体としての設計思想は OLED 研究とも強く重なります。
シクロデキストリンを含むバイオポリマーとの複合化という考え方は、
- 有機ELの発光層や界面層の安定化
- 光取り出し効率の向上
- 環境負荷の小さい材料選択
といった観点で、有機ELにも応用可能なコンセプトと言えます。
日本語まとめ
このレビュー論文からわかることをまとめると:
- 金属ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトは、よく光る・色がきれい・作りやすいという大きな魅力がある一方、
水・酸素・熱・光に弱いという弱点も持つ。 - 高分子・バイオポリマー(デンプン、シクロデキストリン、ポリ乳酸など)と組み合わせることで、
安定性と加工性を高めた複合材料にできる。 - 特にシクロデキストリンは、ホスト–ゲスト構造を活かしてペロブスカイトを「包み」、
光る材料や電極界面をやさしく制御するツールとして有望である。 - これらの戦略は、ペロブスカイトLEDだけでなく、有機ELを含む
次世代の環境調和型光デバイスの設計にもつながっていく。
Metal Halide Perovskites and Cyclodextrin-based Composites (English)
Scope of this page
This page summarizes a single review article contained in the Web of Science file
OLED_CD_review.txt, written by Farfan et al., and reorganizes it into
three themes that are particularly relevant to OLED and light-emitting devices.
The three themes are:
- What are metal halide perovskites?
- Composites with polymers and biopolymers (including cyclodextrin)
- Applications to light-emitting devices and future perspectives
1. What are metal halide perovskites?
Metal halide perovskites are semiconductor materials with a perovskite-type crystal structure,
typically composed of:
- metal cations (Pb, Sn, Ge, etc.),
- halides (Cl, Br, I), and
- organic or inorganic A-site cations (e.g., FA, MA, Cs).
According to the review, they are highly attractive because they offer:
- high photoluminescence efficiency,
- narrow emission linewidths (high color purity), and
- solution-processability at low cost.
These properties make them ideal for solar cells, lasers, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
2. Composites with polymers and biopolymers — role of cyclodextrin
The stability challenge
Despite their excellent optical and electronic properties,
metal halide perovskites are sensitive to moisture, oxygen, heat, and light,
which leads to rapid performance degradation.
Improving stability and durability is therefore a central theme of the review.
Polymer and biopolymer composites
Farfan et al. summarize many studies in which perovskites are combined with:
- conventional polymers (e.g., PMMA, PVDF), and
- biopolymers such as starch, cyclodextrin, polylactic acid, and polylysines.
These composite systems can:
- control crystal growth and particle size,
- passivate and protect the perovskite surface from moisture and oxygen,
- form flexible, processable films for large-area coatings.
Cyclodextrin-containing materials
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are cyclic oligosaccharides with a cavity that can host ions or small molecules.
The review highlights CDs as part of the family of biopolymers used to:
- surround and stabilize perovskite precursors or nanocrystals,
- influence nucleation and growth,
- improve environmental stability.
In this way, CD-containing composites offer a promising route towards
greener and more robust perovskite-based light-emitting materials.
3. Applications to LEDs and display technologies
Perovskite LEDs (PeLEDs)
The review discusses the application of metal halide perovskites to:
- high-brightness, high-color-purity PeLEDs,
- display backlights and pixel emitters,
- and other photonic devices such as lasers.
Perovskite nanocrystals embedded in polymer or biopolymer matrices can provide:
- efficient light emission,
- improved stability,
- easy film processing over large areas.
Links to OLED research
Although perovskites are not classical organic emitters, many device-level issues are shared with OLEDs:
- the need to combine high efficiency and long-term stability,
- the importance of interfacial engineering and energy-level alignment,
- the desire for flexible, solution-processed devices.
Strategies based on cyclodextrin-containing biopolymers for perovskites
can therefore inspire similar approaches in OLED research:
- stabilizing emitting and charge-transport layers,
- improving light outcoupling and durability,
- and moving towards environmentally friendly, sustainable light sources.
English summary
In summary, the review article by Farfan et al. shows that:
- Metal halide perovskites are outstanding light-emitting and photovoltaic materials,
but their environmental instability is a major hurdle. - Combining perovskites with polymers and especially biopolymers
(starch, cyclodextrin, polylactic acid, polylysines) is a powerful way to
enhance their stability, processability, and mechanical properties. - Cyclodextrin-based composites, in particular, can act as protective hosts and
structure-directing agents, paving the way for green and stable perovskite LEDs. - These concepts are highly relevant to OLED and other organic photonic devices,
pointing towards future bright, durable, and eco-friendly light-emitting technologies.
References
- Farfan, H. I.; Roa, K. L.; Castro, H. F.,
“Advances in hybridised and inorganic composite metal halide perovskites: A review”,
Opto-Electronics Review 31, e148221 (2023).
DOI: 10.24425/opelre.2023.148221.