CD Reviews(Cyclodextrin Reviews)|一般向け解説(日本語+English)
参照文献は 添付ファイル CD_Reviews.txt に含まれる3報のみです。
This page is based only on the three review papers listed in CD_Reviews.txt.
日本語(JP)
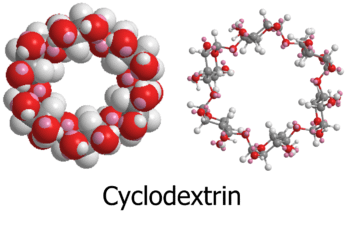
1. まず結論:シクロデキストリン(CD)は「分子サイズの入れ物」
シクロデキストリン(Cyclodextrin, CD)は、ドーナツ状の“分子のカップ”のような構造を持ちます。
内側(空洞)が疎水性っぽく、外側が親水性っぽいので、水に溶けにくい分子を“中に入れて”水に分散させやすくできます。
この「包接(ほうせつ)=inclusion complex」作用は、特に溶けにくい薬(難溶性薬物)の扱いで重要です。
多くの場合、薬とCDは 1:1 の比で複合体を作ります。
また、天然のCDは水中で自己会合(集まりやすい)性質があり、これが溶解性を制限する要因になることがあります。
一方で、誘導体化(置換基の導入)により溶けやすさや包接能を改善でき、ただし効果は置換基の種類・置換度に依存します。
(Saokham らの総説より)
2. 「CDを入れれば万能」ではない:製剤では“バランス設計”が大事
CDは薬を溶かすのに役立ちますが、入れ過ぎると逆効果になる場合があります。
理由の一つは、CDが薬を抱え込むことで、膜を通って体内に入る“自由な薬”の割合が変わりうるためです。
また、製剤に入る他の添加剤(高分子、保存料、界面活性剤など)もCDと相互作用し、薬と添加剤がCDを取り合う(競合包接)ことがあります。
(Saokham らの総説より)
実務的な言い方をすると:
「溶ける」+「届く」+「安定」 の3つを同時に満たすように、CD量と配合を最適化します。
3. CD×キトサン:粘膜に“とどめて効かせる”方向の工夫
口・鼻・目・腸などの粘膜(mucosa)は薬の投与ルートとして重要ですが、流れやすく滞在時間が短いのが課題です。
そこでムコアドヒージョン(粘膜付着性)を持つ材料が使われます。
キトサンは代表的な粘膜付着性高分子ですが、中性〜塩基性で溶けにくいなどの弱点があり、さまざまな誘導体化で改善が試みられています。
その中に cyclodextrin-chitosan(CD-キトサン)のような設計も含まれます。
(Ways らの総説より)
イメージ:
CDが「薬を抱えて運ぶ係」、キトサンが「粘膜に貼り付く係」になり、
“必要な場所に、必要な時間だけ”薬を届けやすくします(考え方)。
4. CDは医薬だけじゃない:材料科学でも“分子添加剤”として働く
CD(例:β-CD)は、医薬分野だけでなく、膜材料(mixed-matrix membrane, MMM)などの材料科学でも登場します。
MMMは、ポリマーに多孔性粒子(MOFなど)や分子添加剤を混ぜ、ガス分離性能などを改善する考え方です。
この分野の総説では、β-CDがキーワードとして挙げられ、分子添加剤を含む広い設計指針が議論されています。
(Dechnik らの総説より)
ここでのポイントは:
CDは「包接」だけでなく、相互作用の調整役(compatibilityの改善など)として材料設計に入ってくることがある、という点です。
5. まとめ(HP用の要点)
- CDは分子を“中に入れる”ことで、難溶性分子の扱いを助ける
- ただし量と配合が重要:添加剤との競合包接にも注意
- CDは医薬(溶解性・粘膜送達)だけでなく、材料(膜など)でも分子設計の部品として使われる
English (EN)
1. Key idea: Cyclodextrins (CDs) are “molecular cups”
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are donut-shaped oligosaccharides that can host guest molecules in their inner cavity.
Because the cavity is relatively hydrophobic while the outer surface is more hydrophilic, CDs can help disperse poorly water-soluble molecules in water by forming inclusion complexes.
For many drug/CD complexes, the most common stoichiometry is 1:1.
Natural CDs may self-assemble (aggregate) in water, which can limit their apparent solubility.
Chemical derivatization can improve solubility and complexation, but the outcome depends on the substituent type and degree of substitution.
(From the review by Saokham et al.)
2. CDs are not “magic”: formulation is about balance
CDs can enhance solubility, but more is not always better.
Complexation can change the fraction of “free” drug available for membrane permeation.
In addition, excipients (water-soluble polymers, preservatives, surfactants, etc.) may interact with CDs, leading to competitive complexation between the drug and excipients.
(From the review by Saokham et al.)
Practical takeaway: optimize CDs to balance solubility, delivery (permeation), and stability.
3. CD–chitosan strategies: “stay longer on mucosa”
Mucosal drug delivery (oral, nasal, ocular, intestinal, etc.) often suffers from short residence time.
Chitosan is a classic mucoadhesive polymer, but it has limitations such as reduced solubility at neutral/basic pH.
Therefore, many chemical modifications have been explored—among them, cyclodextrin–chitosan designs are discussed as part of the broader landscape.
(From the review by Ways et al.)
A simple picture: CDs can support drug handling, while chitosan supports mucoadhesion, potentially improving local retention.
4. Beyond pharma: CDs appear in materials (e.g., mixed-matrix membranes)
CDs (e.g., β-cyclodextrin) also appear in materials science, such as mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) for gas separation.
A major review discusses MMM fabrication and the role of porous fillers and molecular additives; β-CD is included among relevant concepts/keywords.
(From the review by Dechnik et al.)
Key point: CDs can serve not only as host molecules but also as molecular design components that tune interactions/compatibility.
5. Summary for a general audience
- CDs can host molecules and help with poor solubility
- Real formulations require optimization (including competition with other excipients)
- CDs are used in both drug delivery and advanced materials as functional building blocks
References (only from CD_Reviews.txt)
- Saokham, P.; Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. Molecules (2018). DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161
- Ways, T. M. M.; Lau, W. M.; Khutoryanskiy, V. V. Chitosan and Its Derivatives for Application in Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers (2018). DOI: 10.3390/polym10030267
- Dechnik, J.; Gascon, J.; Doonan, C. J.; Janiak, C.; Sumby, C. J. Mixed-Matrix Membranes. Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2017). DOI: 10.1002/anie.201701109