このページは、3報のみをもとに、シクロデキストリン(CD)誘導体/CDポリマー研究の要点を、一般の方向けに整理したものです。
日本語版
1) まず結論(超要約)
- CD(シクロデキストリン)は“輪っか状の糖”で、内側の空洞に分子を取り込み(ホスト–ゲスト相互作用)、包接複合体を作れます。
- 水への溶けやすさ(溶解度)や複合体のふるまいは、CDの種類・置換基・置換度、さらに添加剤(ポリマーや界面活性剤など)で大きく変わります。
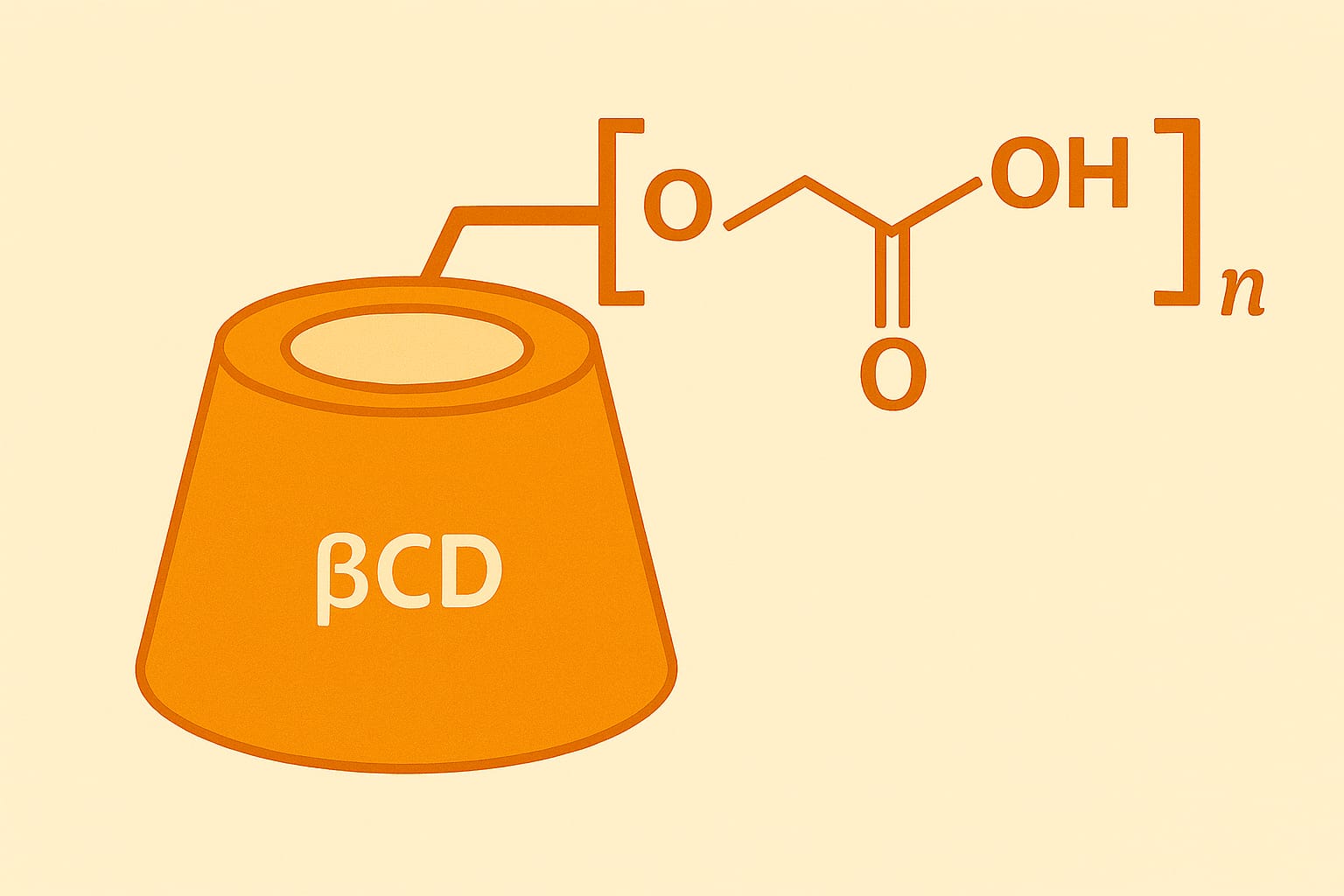
- β-CDポリマー(β-CDP)を材料に組み込むと、例えばハイドロゲルで薬物放出をゆっくりにするなど、機能設計に使えます。
2) 3本の論文を“やさしく”読む
Paper 1:CDと「溶けやすさ」の基本を押さえる
何を扱った?
CDや薬物/CD複合体の溶解度、そして溶解度に影響する要因(CDの自己会合・誘導体化・添加剤など)を整理した総説です。
ポイント(一般向け)
– 多くの薬物/CD複合体は 1:1 の比でできることが多い。
– ただし天然CDは水中で集まりやすく(自己会合・凝集)、それが溶解度を制限する場合がある。
– 置換基を導入した誘導体化で溶解性や複合化能を高められるが、効果は置換基の種類や置換度に依存する。
– 防腐剤・界面活性剤・水溶性ポリマーなどの添加剤は、CDの溶解化能力に影響し得るため、製剤設計では「薬物と添加剤がCDと競合して結合する可能性」も考える必要がある。
ひとこと
「CDを使えば何でも溶ける」ではなく、CD自身の溶け方・集まり方まで含めて設計するのが大切、というメッセージです。
Paper 2:β-CDPを使った“二層ハイドロゲル”で放出制御
何を作った?
β-CDポリマー(β-CDP)とPVA、CMCを用い、層状(ドラッグ放出層+機械支持層)の二層ハイドロゲルを作製。機械強度と耐水性、薬物放出の改善を狙った研究です。
ポイント(一般向け)
– β-CDPを導入することで、薬物放出が遅くなる(持続放出化)。
– 支持層をCaCl₂/ホウ酸溶液に浸漬する処理で、機械強度を強化。
– 二層構造により、引張強度 1504 kPa、破断伸び 400% を達成。
– 放出メカニズムは、従来の単純な拡散モデルではなく、拡散–緩和–侵食が関与するモデルに適合した。
ひとこと
β-CDPは「分子を取り込む」性質を材料側に持たせられるので、“放出をゆっくり”にする設計に活用できます。
Paper 3:CDはどこに使われている?(分子→応用の概観)
何をまとめた?
CDの基本的な特徴(空洞を持つ“かご状分子”)と、近年の多様な応用(医薬、食品、化粧品、触媒、分離、環境など)を俯瞰した総説です。
ポイント(一般向け)
– CDは疎水性の空洞に分子を取り込むことで包接複合体を作り、多方面の応用につながる。
– 応用分野として、薬・医療・食品・化粧品・日用品・触媒・クロマト・バイオ・ナノテク・繊維などが挙げられる。
– “基礎研究の蓄積”と“応用の広がり”の両方が大きい分野であることを強調。
ひとこと
CDは「一部の特殊材料」ではなく、横断的に使われる機能分子として整理されています。
3) 用語ミニ解説(このページに出てきた言葉だけ)
- シクロデキストリン(CD):グルコースが環状につながったオリゴ糖。内側に空洞がある。
- 包接複合体(ホスト–ゲスト):CD(ホスト)の空洞に分子(ゲスト)が取り込まれた状態。
- 自己会合・凝集:CD同士が集まって“かたまり”になりやすい現象。溶解度に影響する。
- 置換基/置換度:CDに付ける官能基、およびその付き方の程度。性質が変わる要因。
- ハイドロゲル:水を多く含むゲル材料。創傷被覆材などで使われる。
参考文献(添付ファイル内の3報のみ)
[1] Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes — MOLECULES (2018) — 23(5) — Article 1161 — DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161 (https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051161)[2] A Double-Layer Hydrogel Dressing with High Mechanical Strength and Water Resistance Used for Drug Delivery — MOLECULES (2023) — 28(2) — Article 499 — DOI: 10.3390/molecules28020499 (https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020499)
[3] Cyclodextrins, from molecules to applications — ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS (2018) — 16(4) — 1361–1375 — DOI: 10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2)
Suggested tags(WP用)
CMβCDP, β-CDP, cyclodextrin, inclusion complex, solubility, hydrogel, drug delivery
English version
1) Take-home messages (very short)
- Cyclodextrins (CDs) are ring-shaped oligosaccharides with a cavity that can encapsulate guest molecules (host–guest inclusion).
- Solubility and complexation behavior depend on CD type, substituents/degree of substitution, and formulation excipients (polymers, preservatives, surfactants).
- Incorporating β-cyclodextrin polymer (β-CDP) into materials (e.g., hydrogels) can help slow drug release while maintaining mechanical performance.
2) What these three papers say (plain-language summaries)
Paper 1: The fundamentals of CD/complex solubility
A review summarizing how CD solubility and drug/CD complex solubility are affected by aggregation, derivatization, and excipients. Key notes include frequent 1:1 complex stoichiometry, possible CD aggregation in water, and the importance of considering competitive complexation between drugs and excipients during formulation.
Paper 2: A β-CDP-based double-layer hydrogel for sustained release
This study reports a double-layer hydrogel (drug release layer + mechanical support layer) made from β-CDP, PVA, and CMC. Adding β-CDP slowed drug release, while post-treatment of the support layer improved mechanical strength. The combined structure achieved 1504 kPa tensile strength and 400% elongation, and the release behavior followed a diffusion–relaxation–erosion model.
Paper 3: From CD molecules to broad applications
A review highlighting CDs as “cage-like” molecules forming inclusion complexes and outlining applications across pharmacy/medicine, foods, cosmetics, catalysis, chromatography, biotechnology, nanotechnology, textiles, and more, emphasizing both fundamental and applied research momentum.
References (only the three records in the attached file)
[1] Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes — MOLECULES (2018) — 23(5) — Article 1161 — DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161 (https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051161)[2] A Double-Layer Hydrogel Dressing with High Mechanical Strength and Water Resistance Used for Drug Delivery — MOLECULES (2023) — 28(2) — Article 499 — DOI: 10.3390/molecules28020499 (https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020499)
[3] Cyclodextrins, from molecules to applications — ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS (2018) — 16(4) — 1361–1375 — DOI: 10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2)