[“Cyclodextrin”, “βCD”, “CM-β-CD”, “Polymer”, “Host–Guest”, “Review”]
このページは、総説(Review)3報だけを材料に「シクロデキストリン(CD)」の基礎と、水溶性誘導体・ポリマー(例:CM-β-CDP)の位置づけを、一般向けにまとめたものです。
まず結論(ここがポイント)
- CDは“分子を包む”天然由来ホスト分子:香り・薬・色素などの性質(溶けやすさ、安定性、反応性)を変えられます。
- 誘導体化(HP化、SBE化、CM化など)で“水に溶ける/使いやすいCD”へ:用途(医薬・環境・材料)に合わせて設計します。
- ポリマー化(〜CDP)で“多数の空洞を持つ材料”へ:分子を複数同時に保持したり、膜・ゲルなどの形に加工しやすくなります。
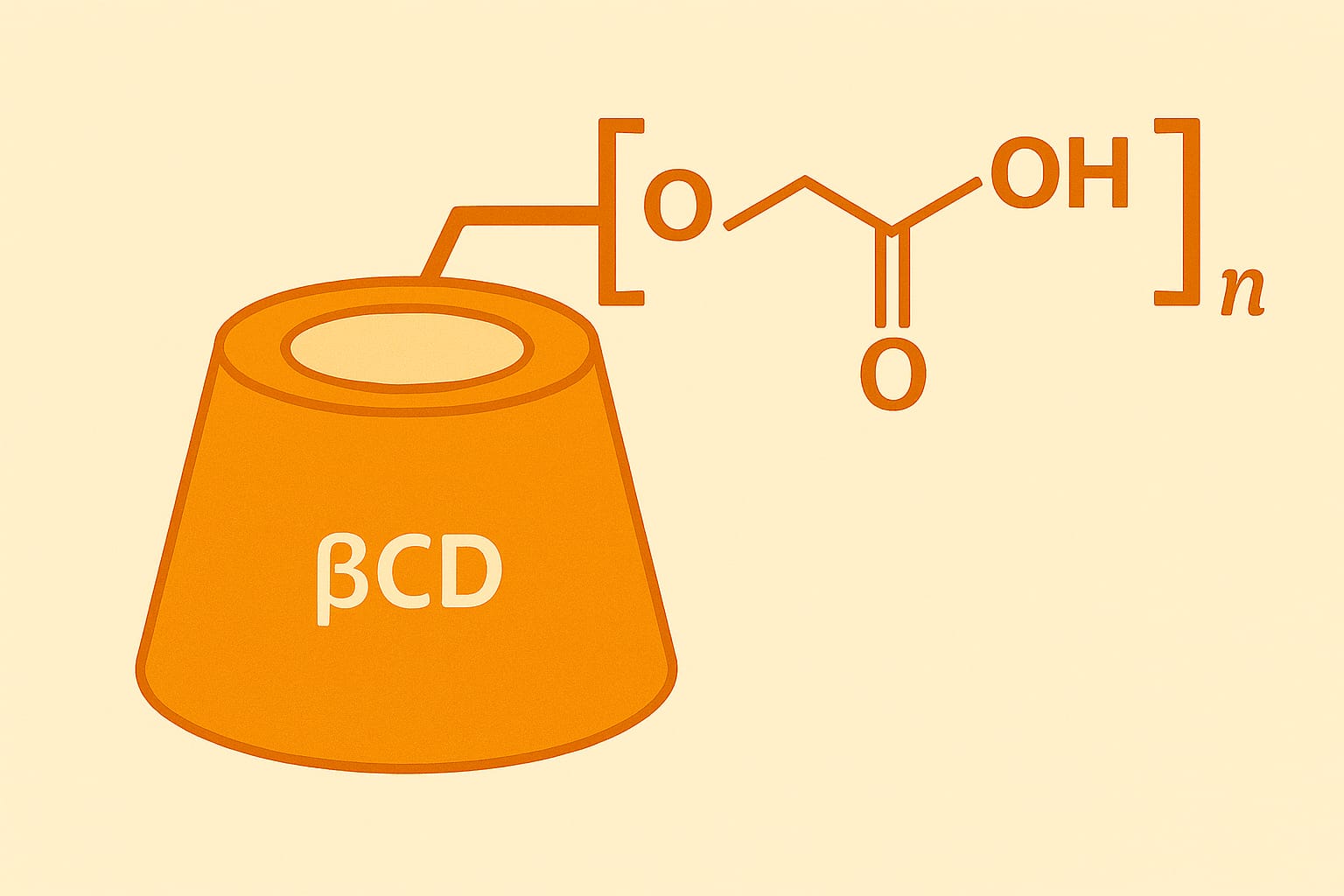
CM-β-CDPって何?(やさしい説明)
シクロデキストリンはドーナツ状の分子で、真ん中の“空洞(キャビティ)”に別の分子を取り込めます。
一方で、βCDそのものは水への溶けやすさに限界があり、現場では水溶性を上げた誘導体がよく使われます。
CM-β-CD(カルボキシメチル化βCD)や、それを材料として扱いやすくしたポリマー(CM-β-CDP)は、
「CDの包接能」+「水系での使いやすさ」+「材料化(膜・粒子・ゲル等)のしやすさ」を両立させる発想の延長線上にあります。
収録3報から読み解く“設計の勘どころ”
1) まずは“溶ける/溶けない”を支配する因子(溶解度・複合体化)
CDが便利でも、目的分子(ゲスト)が水に溶けなければ扱いづらい場面が多いです。
溶解度・複合体(包接体)の作り方・評価(例:相溶解度解析)の考え方を押さえると、誘導体やポリマーを選ぶ理由が明確になります。
2) 応用は“医薬・環境・材料”にまたがる(分野横断性)
CD研究は、薬の溶解性向上・送達(Drug Delivery)だけでなく、環境浄化、分析、機能材料へと広がっています。
CM-β-CDPのような材料は、こうした分野横断のニーズ(安全性・水系処理・材料化)と相性が良い領域です。
3) “分子を包む”が、安定化・機能化の入口になる
包接により、ゲスト分子の分解抑制、揮発抑制、取り扱い性向上などが期待されます。
ポリマー化すると、複数サイトでの保持や、材料としての形状制御にも発想が広がります。
ピックアップ文献 3本(解説付き)
Paper 1
書誌:Saokham, P, Muankaew, C, Jansook, P, Loftsson, T (2018). Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. MOLECULES 23(5) Article 1161
DOI:10.3390/molecules23051161 (https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051161)
なぜ選んだ?:CDとゲスト分子の“溶ける/溶けない”を、実務目線で整理した総説です。
医薬など“水に溶けにくい分子”を扱う場面で、CD(および誘導体)をどう使うかの基本がまとまっています。
HP向けの読みどころ
– CDと複合体の溶解度に影響する要因(CD種類、誘導体化、濃度など)の整理
– 包接体の評価の考え方(溶解度曲線など)
– 水溶性誘導体を使う“必然性”が腹落ちする
Paper 2
書誌:Crini, G, Fourmentin, S, Fenyvesi, É, Torri, G, Fourmentin, M, Morin-Crini, N (2018). Cyclodextrins, from molecules to applications. ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS 16(4) 1361–1375
DOI:10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2)
なぜ選んだ?:CD研究の“全体地図”を短時間でつかめる俯瞰レビューです。
医薬・食品・化粧品・環境・材料など、応用分野の幅広さが分かります。
HP向けの読みどころ
– CDの基本構造と、誘導体化の考え方
– 応用分野別の代表例(アイデア出しに便利)
– “分子から材料へ”の流れ(ポリマー・ナノ材料など)
Paper 3
書誌:Sharma, N, Baldi, A (2016). Exploring versatile applications of cyclodextrins: an overview. DRUG DELIVERY 23(3) 739–757
DOI:10.3109/10717544.2014.938839 (https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.938839)
なぜ選んだ?:CDを“ドラッグデリバリーの道具”として捉え、応用設計を俯瞰できる総説です。
包接によるバイオアベイラビリティ向上など、実装に近い視点が得られます。
HP向けの読みどころ
– 包接が“溶解性・安定性・利用可能性”を変える考え方
– 送達・放出制御など、機能化の方向性
– CD材料を使うときの注意点(選択・安全性・設計)
用語ミニ解説
- 包接(inclusion complex):CDの空洞にゲスト分子が取り込まれた状態。
- ホスト–ゲスト化学:分子同士が“はまり込む”非共有結合相互作用で機能を生む考え方。
- 水溶性CD誘導体:HP-β-CD、SBE-β-CD、CM-β-CDなど。置換基で水への溶解性や相互作用が変わります。
- CDポリマー(〜CDP):CD骨格を材料化したもの(架橋・重合など)。多数のキャビティを持つ材料として設計できます。
参考文献(添付ファイル収録の3報)
- Saokham, P, Muankaew, C, Jansook, P, Loftsson, T (2018). Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. MOLECULES. 23(5): Article 1161. DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161
- Crini, G, Fourmentin, S, Fenyvesi, É, Torri, G, Fourmentin, M, Morin-Crini, N (2018). Cyclodextrins, from molecules to applications. ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS. 16(4): 1361–1375. DOI: 10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2
- Sharma, N, Baldi, A (2016). Exploring versatile applications of cyclodextrins: an overview. DRUG DELIVERY. 23(3): 739–757. DOI: 10.3109/10717544.2014.938839
English
Cyclodextrins & CM‑β‑CDP: Three review papers (from the attached WoS file)
This page is written only from the three review articles included in the attached Web of Science-formatted file.
It introduces the basics of cyclodextrins (CDs) and clarifies why water-soluble derivatives and CD-based polymers (e.g., CM‑β‑CDP) are attractive from an application viewpoint.
Key takeaways
- Cyclodextrins are “molecular containers.” They can host guest molecules (fragrances, drugs, dyes), altering solubility and stability.
- Derivatization (HP-, SBE-, CM-, etc.) makes CDs more usable in water. Selection depends on the target molecule and the application.
- Polymerization (CDP) turns CDs into materials. Multiple cavities in one material enable practical formats such as films, particles, and gels.
What is CM‑β‑CDP in plain words?
Cyclodextrins are doughnut-shaped sugar molecules with an internal cavity that can include other molecules.
Native β‑cyclodextrin may have limited solubility in water, so water-soluble derivatives are widely used in practice.
CM‑β‑CD (carboxymethylated β‑CD) and its polymeric forms (CM‑β‑CDP) aim to combine:
the inclusion capability of CDs + better handling in aqueous systems + easier material processing (films/particles/gels).
Design lessons implied by the three reviews
- Solubility is the starting point. Understand what controls CD/guest solubility and complex formation, then choose derivatives/polymers rationally.
- Applications are cross-disciplinary. CDs span drug delivery, environmental, analytical, and materials science—useful context for positioning CM‑β‑CDP.
- Inclusion enables stabilization and functionality. Complexation can suppress degradation/volatilization and improve usability; polymer formats broaden design options.
Highlighted papers (with plain-language notes)
Paper 1
Bibliographic info: Saokham, P, Muankaew, C, Jansook, P, Loftsson, T (2018). Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. MOLECULES 23(5) Article 1161
DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161 (https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051161)
(Web of Science: WOS:000435204000176 / Times cited: 572)
Why this one? A practical review focusing on CD solubility and CD/guest complexes—essential for choosing derivatives.
Useful points for a lab/HP audience
– Factors controlling solubility and complexation
– How to think about phase-solubility/complex evaluation
– Why water-soluble derivatives are often necessary
Paper 2
Bibliographic info: Crini, G, Fourmentin, S, Fenyvesi, É, Torri, G, Fourmentin, M, Morin-Crini, N (2018). Cyclodextrins, from molecules to applications. ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS 16(4) 1361–1375
DOI: 10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2)
(Web of Science: WOS:000451136500013 / Times cited: 263)
Why this one? A broad overview of cyclodextrins, bridging fundamentals and applications across fields.
Useful points for a lab/HP audience
– CD basics and derivatization concepts
– Application map (ideas for positioning)
– The trend from molecules to materials (polymers/nanotech)
Paper 3
Bibliographic info: Sharma, N, Baldi, A (2016). Exploring versatile applications of cyclodextrins: an overview. DRUG DELIVERY 23(3) 739–757
DOI: 10.3109/10717544.2014.938839 (https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.938839)
(Web of Science: WOS:000370875100005 / Times cited: 189)
Why this one? An application-driven overview focusing on drug delivery—how inclusion improves practical performance.
Useful points for a lab/HP audience
– Inclusion as a route to improve solubility/stability/bioavailability
– Functionalization directions (delivery/release concepts)
– Considerations for selecting CD-based carriers
References (only the three papers in the attached file)
- Saokham, P, Muankaew, C, Jansook, P, Loftsson, T (2018). Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. MOLECULES. 23(5): Article 1161. DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161
- Crini, G, Fourmentin, S, Fenyvesi, É, Torri, G, Fourmentin, M, Morin-Crini, N (2018). Cyclodextrins, from molecules to applications. ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS. 16(4): 1361–1375. DOI: 10.1007/s10311-018-0763-2
- Sharma, N, Baldi, A (2016). Exploring versatile applications of cyclodextrins: an overview. DRUG DELIVERY. 23(3): 739–757. DOI: 10.3109/10717544.2014.938839