最終更新:2026-01-03
本ページは、添付ファイル(Web of Science 出力)に含まれる3報のみを対象に、一般の方にも読みやすい形でポイントをまとめた解説です。
(※医療・健康に関する内容は研究紹介であり、治療や使用を推奨するものではありません)
まず結論:HP-β-CDは「包み込む」分子設計で、食品・薬・生命科学までつながる
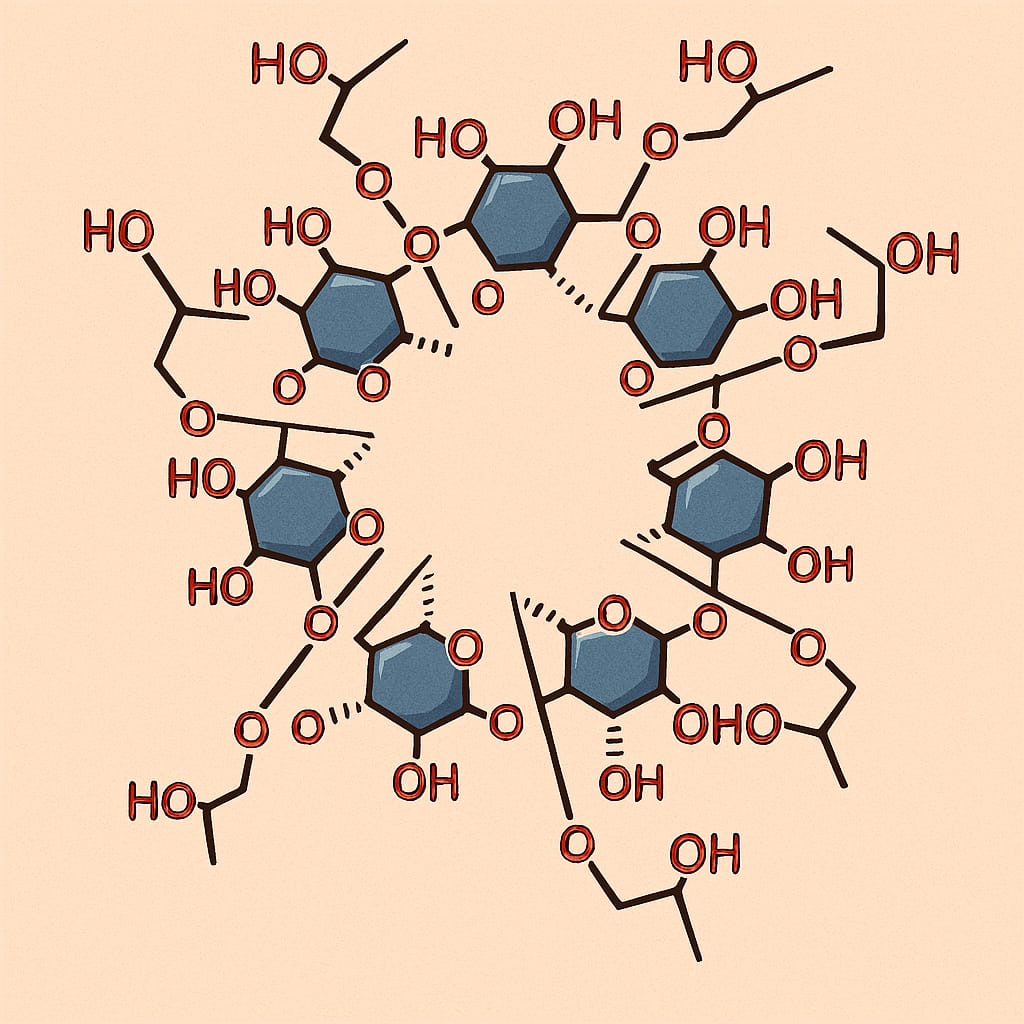
- シクロデキストリン(CD)は、ドーナツ状の分子で、内側の空洞に分子を取り込む 包接(inclusion) ができます。
- HP-β-CD(2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin)は、β-CDを改良して水に溶けやすくした代表的な誘導体の一つです。
- 「溶けにくい/扱いにくい分子を、溶かしやすく・安定に・機能的にする」ための道具箱として、幅広い分野で使われます。
3本の論文を、やさしく読む
論文1:食品分野でのCD包接(Food Chemistry, 2022)
何をまとめたレビュー?
食品成分や香り成分などをCDで包接して、溶けやすさ・安定性・保存性(風味の保持など)を改善する研究を整理したレビューです。
「どうやって包接体を作るのか」「本当に包接しているとどう確認するのか」という、実験の基本プロセスが一通りまとめられています。
一般向けポイント
– 香り成分や機能性成分は、空気や光で劣化しやすいことがあります。CD包接は、そうした成分を“守る”工夫になり得ます。
– 食品・サプリでは「苦味をマスクする」「香りを長持ちさせる」など、体感しやすい効果につながることがあります。
論文2:CD/薬物包接体の“溶解性”の考え方(Molecules, 2018)
何をまとめたレビュー?
CDが薬物分子を包接して、溶けにくい薬を溶けやすくするための考え方を、物性(溶解・会合・添加剤の影響など)から整理したレビューです。
特に、天然CDが水中で集合(会合)して溶けにくくなる場合があり、誘導体化(HP-β-CDなど)で改善できる、という議論が含まれます。
一般向けポイント
– ただCDを足せば良いわけではなく、“最適量”が重要です(入れすぎると狙い通りにならない場合もある)。
– 製剤には高分子や界面活性剤などの添加物が入ることが多く、CDとの“競合”も考える必要がある、とまとめられています。
論文3:HP-β-CDの“溶かす力”を生命科学へ(Science Translational Medicine, 2016)
どんな研究?(記事論文)
HP-β-CDがコレステロールの溶解性を高める性質に注目し、動脈硬化モデルでの影響を調べた研究です。
マウス実験でプラークの性状変化や炎症関連の応答に関する解析が報告され、HP-β-CDが免疫細胞のふるまい(マクロファージなど)に関係する可能性が議論されています。
一般向けポイント(注意つき)
– これは基礎〜橋渡し研究であり、研究内容の紹介です(個人の治療判断には使えません)。
– ここで重要なのは「CD誘導体の“溶かす・運ぶ”能力が、生命現象の理解にも使われる」という学術的な広がりです。
3報から見える“共通メッセージ”
- (1) 作る → (2) 確認する → (3) 機能を評価する:CD研究の基本はこの流れ。
- 溶解性・安定性の改善は、食品にも医薬にも共通の価値。
- 誘導体(HP-β-CDなど)は、天然CDの弱点(溶けにくさ・会合など)を補うために重要。
参考文献(添付ファイル内の3報)
- Cyclodextrins inclusion complex: Preparation methods, analytical techniques and food industry applications
FOOD CHEMISTRY, 2022, 384, 132467
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132467 - Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes
MOLECULES, 2018, 23(5), 1161
DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161 - Cyclodextrin promotes atherosclerosis regression via macrophage reprogramming
SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE, 2016, 8(333), 333ra50
DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad6100
English Version
HP-β-CD (Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin) & Cyclodextrins: Learning from Three Representative Classic Papers
Last updated: 2026-01-03
This page is a plain‑language summary based only on the three papers listed in the attached Web of Science export.
(Medical/health‑related notes are for research communication only, not medical advice.)
Key idea: HP‑β‑CD is a ‘molecular host’ that connects food, pharmaceutics, and life science
- Cyclodextrins (CDs) are donut‑shaped molecules that can form inclusion complexes with guest molecules.
- HP‑β‑CD (2‑hydroxypropyl‑β‑cyclodextrin) is a widely used β‑CD derivative designed to be more water‑soluble.
- CDs are often used as a practical toolkit to improve solubility, stability, handling, and functional performance.
The three papers (plain‑language summaries)
Paper 1 (Food Chemistry, 2022): CD inclusion complexes for food applications
This review summarizes how CD inclusion can help improve solubility, stability, shelf‑life, and sensory properties of food‑related compounds (e.g., flavors). It also organizes common preparation methods and analytical techniques used to confirm inclusion.
– Takeaway: CD inclusion is a practical approach to protect sensitive ingredients and modulate taste/odor.
Paper 2 (Molecules, 2018): Solubility of CDs and drug/CD complexes
This review focuses on the physicochemical basis of using CDs to improve poorly soluble drugs, including CD self‑aggregation, derivatization (e.g., HP‑β‑CD), and the impact of excipients such as water‑soluble polymers and surfactants.
– Takeaway: optimization (including the amount of CD and formulation context) is essential.
Paper 3 (Science Translational Medicine, 2016): HP‑β‑CD in translational life‑science research
This research article investigated how HP‑β‑CD, known to increase cholesterol solubility, affects biological processes in an atherosclerosis model, including analyses related to immune cell behavior.
– Takeaway: CD derivatives can be research tools beyond formulation—extending into mechanistic biology (not a clinical recommendation).
A shared message across the three papers
- A common workflow is (1) make the complex → (2) verify inclusion → (3) evaluate function.
- Solubility and stability improvements are cross‑cutting benefits in both food and pharmaceutics.
- Derivatives like HP‑β‑CD help overcome limitations of native CDs in water.
References (only the three papers in the attached file)
- Cyclodextrins inclusion complex: Preparation methods, analytical techniques and food industry applications
FOOD CHEMISTRY, 2022, 384, 132467
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132467 - Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes
MOLECULES, 2018, 23(5), 1161
DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051161 - Cyclodextrin promotes atherosclerosis regression via macrophage reprogramming
SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE, 2016, 8(333), 333ra50
DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad6100