date: 2026-01-12
tags: [Spiropyran, スピロピラン, Electrochemistry, 電気化学, CO2利用, Electrocarboxylation, 分子スイッチ, Smart surface]
一般の方向けにわかりやすく解説します。
研究のねらいを一言で
CO₂(空気中の二酸化炭素)を“原料”として使い、スピロピラン分子スイッチを電気化学的にカルボキシ化(–CO₂H を導入)する研究です。
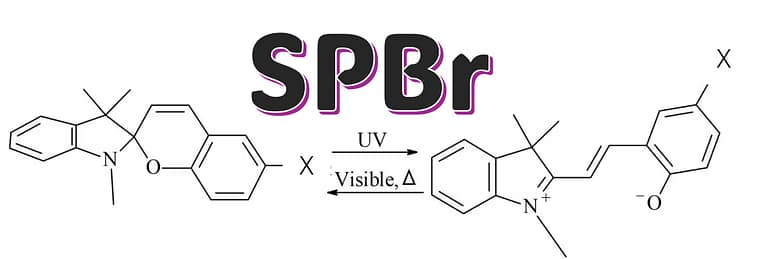
スピロピラン(Spiropyran)って?
スピロピランは、光などの刺激で形が変わり、色や性質が切り替わる「分子スイッチ」として知られています。
この研究では、炭素–臭素(C–Br)結合をもつスピロピラン(Br-BIPS)を出発物質として使います。
“電気化学的カルボキシ化(electrocarboxylation)”とは?
ざっくり言うと、次の2段階です。
- 電極で電子を与えて(還元して)反応を起こす
- 反応途中でできた活性種が CO₂ と反応して –CO₂ 基を導入する
→ こうして C–C 結合形成を進め、CO₂を「価値ある化学品」の骨格に取り込む発想です。
この論文のポイント(一般向け)
1) まず“切る”:C–Br結合の開裂(debromination)
論文では、Br-BIPS の電気化学的還元を調べ、C–Br結合が切れる反応機構を明らかにした上で、カルボキシ化へ進めています。
2) 電極(カソード)の違いが効く
グラッシーカーボン(ガラス状炭素)と銀(Ag)の2種類の電極を用い、
C–Br開裂における電極材料の役割を比較しています。
3) そして“つける”:CO₂を使ってカルボキシ化体を合成
電極の役割が理解できた後、CO₂雰囲気下で電気化学的カルボキシ化を行い、
カルボキシ化スピロピラン誘導体を(著者要約では)「中程度の収率・転化率」で合成できることを示しています。
4) 何がうれしい?—「スマート表面」設計への道
著者要約では、この“グリーン”な合成ルートが、切り替え可能な物性をもつスマート表面の設計に向けた持続可能な戦略になり得る、と述べられています。
(たとえば、表面に固定化した分子スイッチの機能設計などを想定)
用語ミニ解説
- 電気化学(electrochemistry):電極で電子を出し入れして反応を進める化学
- 還元(reduction):電子を与えること
- カソード(cathode):還元が起こる側の電極
- カルボキシ化(carboxylation):分子に –CO₂(最終的に –CO₂H など)を導入すること
- CO₂利用(CCU):CO₂を回収・利用し、化学品や材料に変換する考え方
参考文献(添付ファイル内)
- Santiago, S, Richart, C, Mena, S et al.. Electrocarboxylation of Spiropyran Switches through Carbon-Bromide Bond Cleavage Reaction. Chemelectrochem (2022) 9(8) Article e202101559. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202101559
English (for your website)
Scope
This page summarizes only the record contained in the attached file SPBr.txt (Web of Science export).
Because the file includes one paper, we provide a clear, expanded explanation of that single study.
One-sentence goal
The study demonstrates electrocarboxylation of a spiropyran molecular switch (Br-BIPS) by leveraging carbon–bromine (C–Br) bond cleavage and using CO₂ as a C1 building block to form a new C–C bond.
What is a spiropyran?
Spiropyrans are well-known molecular switches whose structure (and often optical/physical properties) can be reversibly changed by external stimuli such as light.
Here, the starting switch is a brominated spiropyran (Br-BIPS) featuring a C–Br bond that can be activated electrochemically.
What is electrocarboxylation?
In simple terms, electrocarboxylation is:
- Generate reactive intermediates electrochemically (by reduction at a cathode)
- Trap those intermediates with CO₂ to introduce a carboxylate/carboxyl group
→ a strategy for CO₂ capture and utilization (CCU) to build value-added molecules.
Key messages from the paper
1) Mechanistic insight first: electrochemical C–Br bond cleavage
The authors investigate the electrochemical reduction of Br-BIPS and clarify the reduction pathway leading to C–Br bond cleavage, before applying CO₂ for carboxylation.
2) The cathode matters
Two cathodes are compared—glassy carbon and silver—to understand how electrode materials affect the debromination step.
3) CO₂ incorporation: synthesis of carboxylated spiropyran derivatives
With the cathode role clarified, the study reports electrocarboxylation under CO₂ to obtain carboxylated spiropyran derivatives (described in the abstract as moderate yields and conversion rates).
4) Why it matters: toward sustainable “smart surfaces”
The authors describe the approach as a green, efficient route that could enable sustainable strategies for designing smart surfaces with switchable physical properties.
Reference (from the attached file)
- Santiago, S, Richart, C, Mena, S et al.. Electrocarboxylation of Spiropyran Switches through Carbon-Bromide Bond Cleavage Reaction. Chemelectrochem (2022) 9(8) Article e202101559. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202101559