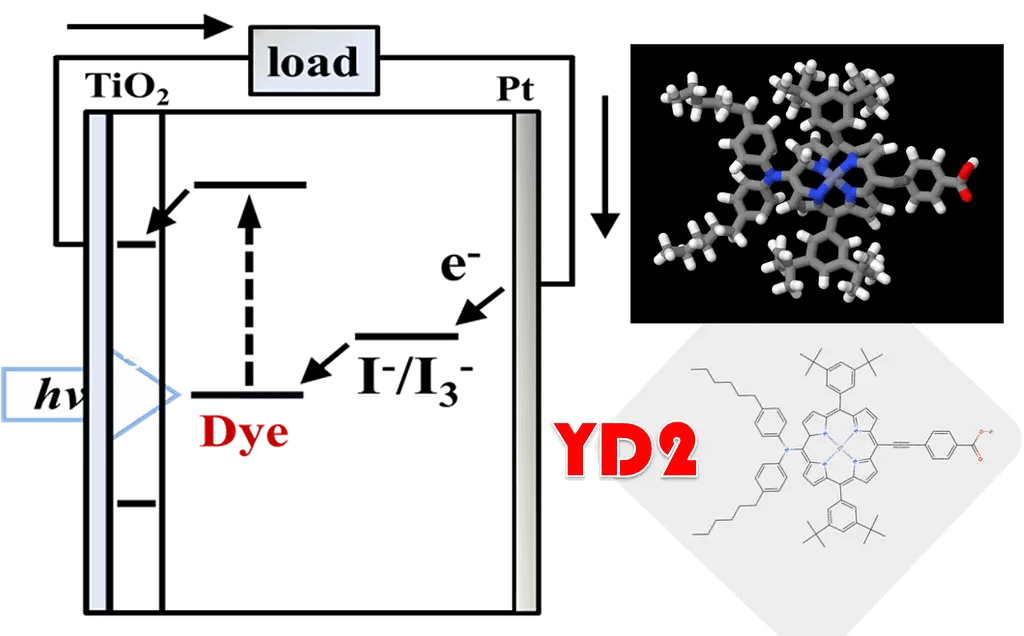
日本語版:色素増感太陽電池(DSSC)とは?
色素増感太陽電池(Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell, DSSC)は、「色素」が光を吸収して電気エネルギーに変える有機系太陽電池です。
シリコン太陽電池と比べて変換効率はまだ低めですが、
- カラフルな発電ガラスとしてデザイン性が高い
- 室内の弱い光でも発電しやすい
- 将来的に低コストで作れる可能性がある
といった特色から、次世代の分散電源として注目されています。
1. DSSCの基本構造(やさしいイメージ)
DSSCはざっくり言うと「サンドイッチ構造」の太陽電池です。
- 色素分子:光を吸収して電子を励起する主役(色をつくる分子)
- 酸化物半導体(多くはTiO₂):色素から電子を受け取り、電気の通り道をつくる白いスポンジ電極
- 電解質:電子を失った色素に電子を戻す「電子のバトン渡し役」
- 透明導電ガラス/カウンター電極:外から光を入れ、外部回路に電流を取り出すための電極
光が当たると、
色素 → 酸化物半導体 → 外部回路 → カウンター電極 → 電解質 → 色素
というループで電子が流れ、電力として利用できます。
2. レビュー論文から見るDSSC研究の流れ
2-1. 全体像をつかむレビュー
Sharma ら, “Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: Fundamentals and Current Status”(Nanoscale Research Letters, 2018)
このレビュー論文では、
- DSSCの基本原理(光吸収・電子注入・再結合)
- 色素・酸化物半導体・電解質・電極材料のバリエーション
- 変換効率を高める工夫と、長期安定性の課題
- レアメタル削減や環境負荷低減を目指した材料設計
など、DSSC研究の「地図」をコンパクトに整理しています。
DSSCの全体像を把握したい読者にとって、最初に読むレビューとして非常に有用です。
2-2. カウンター電極に焦点を当てたレビュー
Wu ら, “Counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells”(Chemical Society Reviews, 2017)
DSSCでは、光を受ける「色素側」の電極だけでなく、
カウンター電極(対極)も性能とコストを左右する重要なパーツです。
このレビューでは、
- 白金(Pt)電極の長所と、コスト・資源の問題
- カーボン材料(カーボンブラック、グラファイト、カーボンナノチューブなど)
- 導電性高分子や金属硫化物・金属窒化物といった代替材料
- 触媒活性と電気抵抗のバランス設計
が詳しくまとめられています。
「どの材料で、どこまでPtを減らせるか?」という視点は、
実用化・量産化を考えるうえで非常に重要です。
2-3. 解析手法としてのインピーダンス測定レビュー
Laschuk ら, “Reducing the resistance for the use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis in materials chemistry”(RSC Advances, 2021)
DSSCの中で「電気がどこで流れにくくなっているか?」を調べる代表的な方法が
交流インピーダンス測定(EIS)です。
Laschuk らの論文は、材料化学分野でEISを使うときに感じやすい「とっつきにくさ」を減らすことを目的としたレビューで、
- 抵抗やキャパシタンスを等価回路として表す考え方
- ナイキストプロット(半円グラフ)の読み方
- データ解析でつまずきやすいポイントと、その回避方法
をやさしく整理しています。
DSSC研究でもEISは必須の評価法であり、
「太陽電池の中の電気の渋滞」を見える化するための重要なツールです。
3. 日常生活とのつながり
紹介したレビュー論文から見えるDSSCの魅力を、日常生活のイメージでまとめると:
- 発電するインテリア:色やデザインを自由に変えられるので、窓・パーテーション・看板などと組み合わせた発電が可能。
- 室内光で動く小型デバイス:スマートウォッチやセンサー類の「電池いらず」電源として期待。
- 環境に配慮したエネルギー技術:高価でレアな材料を減らしつつ、高効率・長寿命を目指す研究が進んでいる。
4. ここがポイント(日本語まとめ)
- DSSCは、色素が光を吸収して電子を流す「色の太陽電池」であり、デザイン性と低照度での発電が強みです。
- レビュー論文では、色素・電解質・酸化物半導体・電極材料・解析手法まで、デバイス全体を最適化する視点が示されています。
- カウンター電極やインピーダンス解析の工夫は、効率だけでなく、耐久性やコストとの両立を図るために重要な鍵となっています。
English Version: Overview of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs)
1. What is a DSSC?
A dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) is a type of solar cell in which dye molecules absorb light and inject electrons into a wide-bandgap semiconductor such as TiO₂.
Compared with crystalline silicon cells, DSSCs typically show lower efficiency, but they offer:
- High design flexibility (colored or semi-transparent modules)
- Good performance even under low or indoor light
- The potential for low-cost manufacturing in the future
This makes DSSCs attractive for building-integrated photovoltaics and small self-powered devices.
2. Insights from Key Review Articles
2.1 Fundamentals and current status
Sharma et al., “Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: Fundamentals and Current Status” (Nanoscale Research Letters, 2018)
This article provides a concise roadmap of the DSSC field:
- Basic working principles (light absorption, electron injection, transport, and recombination)
- Variations of dyes, semiconductor electrodes, electrolytes, and counter electrodes
- Strategies to improve power conversion efficiency
- Challenges of long-term stability and material sustainability
It is an excellent starting point for readers who want an overview of DSSC research.
2.2 Focus on counter electrodes
Wu et al., “Counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells” (Chemical Society Reviews, 2017)
The counter electrode is as important as the photoanode for overall device performance.
The review discusses:
- Conventional platinum (Pt) electrodes and their cost/resource issues
- Carbon-based materials, conducting polymers, and various inorganic catalysts
- How catalytic activity and electrical resistance of the counter electrode affect device efficiency
- Approaches for reducing Pt usage while maintaining high performance
From a practical viewpoint, this article highlights how electrode design links directly to price and scalability.
2.3 Electrochemical impedance as a diagnostic tool
Laschuk et al., “Reducing the resistance for the use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis in materials chemistry” (RSC Advances, 2021)
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is widely used to analyze DSSCs and other electrochemical devices.
In this tutorial-style review, the authors:
- Explain equivalent circuits in terms of resistors and capacitors
- Show how to interpret Nyquist plots
- Point out common pitfalls in data fitting and how to avoid them
For DSSC researchers, EIS helps to identify where charge transport is limited inside the cell — similar to locating a traffic jam in an electric circuit.
3. Why DSSCs matter
Summarizing the message from these reviews:
- DSSCs connect color, design, and electricity generation in a single device.
- By tuning dyes, semiconductors, electrolytes, and electrodes, researchers aim to balance efficiency, stability, cost, and environmental impact.
- Combined with analytical tools like EIS, DSSC research provides a rich playground where chemistry and device engineering meet.
4. Key takeaways (English)
- DSSCs are dye-based solar cells with high design flexibility and good low-light performance.
- Recent reviews emphasize holistic device design, covering dyes, electrodes, electrolytes, and analysis methods.
- Counter-electrode engineering and impedance spectroscopy are crucial for pushing DSSCs toward practical, low-cost, and durable applications.
参考文献 / References
- Sharma, K.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, S. S. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: Fundamentals and Current Status. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2018, 13, 381. DOI: 10.1186/s11671-018-2760-6.
- Wu, J.-H.; Lan, Z.; Lin, J.-M.; Huang, M.-L.; Huang, Y.-F.; Fan, L.-Q.; Luo, G.-G.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Y.-M.; Wei, Y.-L. Counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46, 5975–6023. DOI: 10.1039/c6cs00752j.
- Laschuk, N. O.; Easton, E. B.; Zenkina, O. V. Reducing the resistance for the use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis in materials chemistry. RSC Advances, 2021, 11, 26054–26064. DOI: 10.1039/d1ra03785d.