Cyclodextrin Organic LED Papers List
| Authors | Author Full Names | Article Title | Source Title | Author Keywords | Keywords Plus | Abstract | Publication Year | Volume | Issue | Article Number | DOI | Number of Pages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
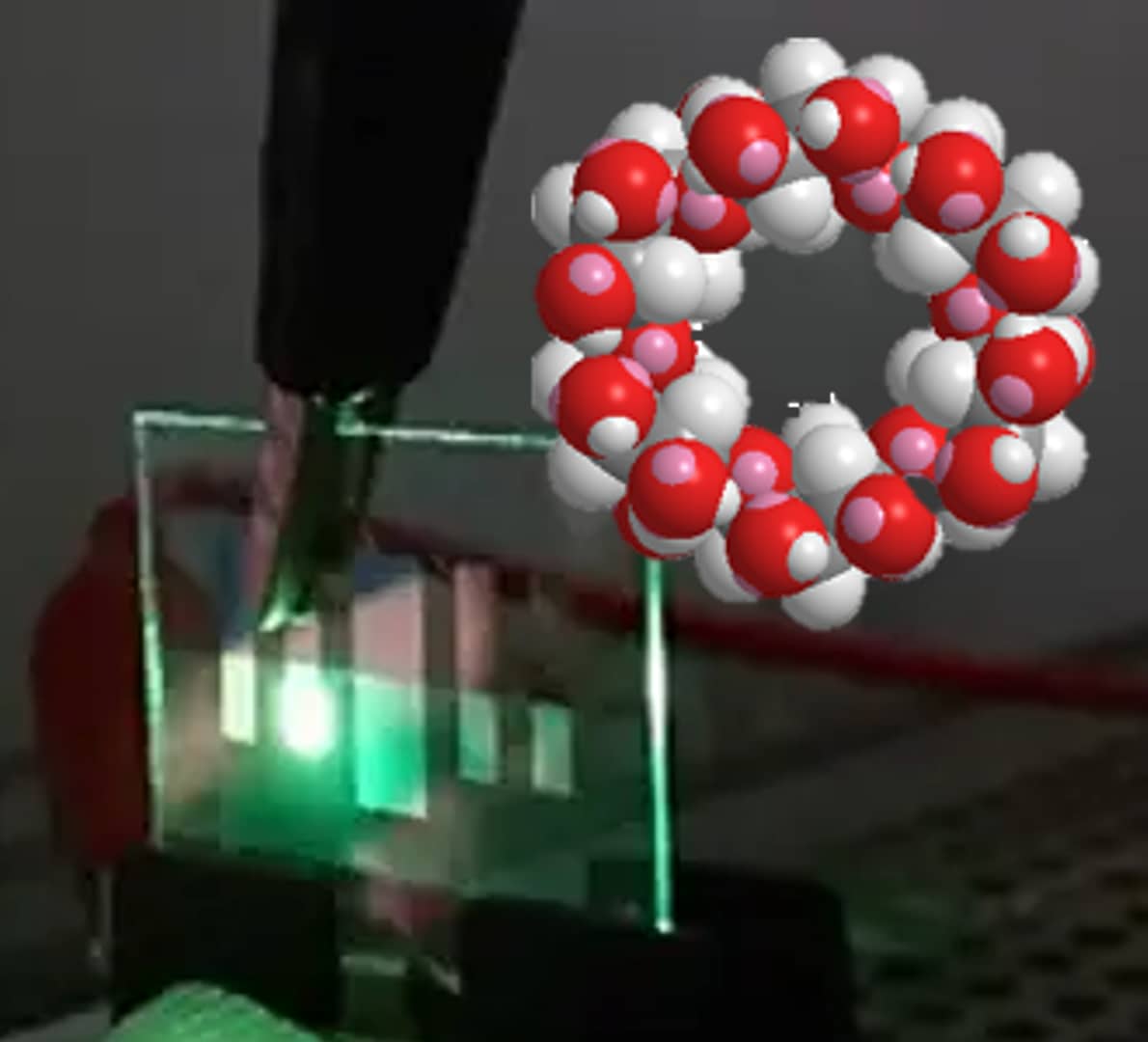
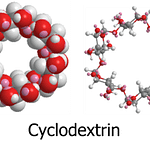
| Hara, M; Umeda, T; Kurata, H | Hara, Michihiro; Umeda, Takao; Kurata, Hiroyuki | Fabrication and Characterisation of Organic EL Devices in the Presence of Cyclodextrin as an Interlayer | SENSORS | organic EL; cyclodextrin polymer; interlayer; energy saving applications | LIGHT-EMITTING-DIODES; HIGHLY EFFICIENT; PERFORMANCE; EMISSION | This study examined glass-based organic electroluminescence in the presence of a cyclodextrin polymer as an interlayer. Glass-based organic electroluminescence was achieved by the deposition of five layers of N,N'-Bis(3-methylphenyl)N,N'-bis(phenyl)-benzidine, cyclodextrin polymer (CDP), tris-(8-hydroxyquinolinato) aluminium LiF and Al on an indium tin oxide-coated glass substrate. The glass-based OEL exhibited green emission owing to the fluorescence of tris-(8-hydroxyquinolinato) aluminium. The highest luminance was 19,620 cd m(-2). Moreover, the glass-based organic electroluminescence device showed green emission at 6 V in the curved state because of the inhibited aggregation of the cyclodextrin polymer. All organic molecules are insulating, but except CDP, they are standard molecules in conventional organic electroluminescence devices. In this device, the CDP layer contained pores that could allow conventional organic molecules to enter the pores and affect the organic electroluminescence interface. In particular, self-association was suppressed, efficiency was improved, and light emission was observed without the need for a high voltage. Overall, the glass-based organic electroluminescence device using CDP is an environmentally friendly device with a range of potential energy saving applications. | 2021 | 21 | 11 | 3666 | 10.3390/s21113666 | 8 |
シクロデキストリンポリマー中間層で拓く低電圧・高輝度有機EL
概要
シクロデキストリンポリマー(CDP)を中間層(インターレイヤー)として導入した有機EL(OLED)の作製と評価を行い、緑色発光(Alq3起因)で最大輝度 19,620 cd m−2を達成しました。CDPの微細孔が有機分子の自己会合や凝集を抑え、界面の発光・電荷再結合を最適化することで、曲げ状態でも 6 V で発光を確認。従来材料(TPD/Alq3/LiF/Al)に植物由来のCDPを組み合わせることで、環境調和とエネルギー効率の両立を指向しています。
ここがポイント
- CDPの包接・多孔ネットワークにより、発光層近傍の分子凝集を抑制し界面を制御。
- Alq3の緑色発光(λmax ≈ 520 nm)を活かし、最大輝度 19,620 cd m−2を実現。
- 曲げ状態でも 6 V で発光を確認し、柔軟デバイス化の可能性を示唆。
- 標準的なOLED構成(ITO/TPD/CDP/Alq3/LiF/Al)にCDPを加えるだけのシンプル実装。
- 植物由来CDPの採用により、環境配慮型デバイスの実装学理を提示。
論文別ハイライト
- 設計/材料:ITO上にTPD(ホール輸送)/CDP(α, β, γ)/Alq3(発光)/LiF/Alの5層を真空蒸着。
- 機能/現象:CDPの孔により分子の自己会合・凝集を抑制、界面での非放射失活を低減。
- 特長/数値:最大輝度 19,620 cd m−2、曲げ状態で 6 V 発光(高効率・低電圧動作を示唆)。
- 用途像:省電力ディスプレイ/照明、フレキシブル表示、環境調和型フォトニクス素子。
用語ミニ解説
- CDP(Cyclodextrin Polymer):CDの水酸基を架橋した三次元多孔体。包接と界面調整に有効。
- インターレイヤー(Interlayer):輸送層と発光層の間に挿入し、電荷注入・再結合・界面失活を制御。
- TPD:N,N′-Bis(3-methylphenyl)-N,N′-bis(phenyl)-benzidine。代表的ホール輸送材料。
- Alq3:tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium。緑色発光を与える発光材料。
- ITO:Indium Tin Oxide。透明導電性電極として広く用いられる。
想定アプリケーション
- 省電力ディスプレイ・照明(低電圧駆動の実現)
- フレキシブル/曲面デバイス(曲げ時の発光安定化)
- 環境調和型エレクトロニクス(植物由来材料の活用)
- 教育・実験用の有機エレクトロニクス教材
関連キーワード
#Cyclodextrin #CDP #OLED #Interlayer #Alq3 #TPD #ITO #GreenEmission #EnergySaving #FlexibleDevice
Cyclodextrin-Polymer Interlayers for Low-Voltage, High-Brightness OLEDs
Overview
We fabricated and evaluated OLEDs integrating a cyclodextrin polymer (CDP) as an interlayer, achieving maximum luminance of 19,620 cd m−2 with green emission from Alq3. The porous CDP suppresses self-association/aggregation of organic molecules and tunes the interface near the emissive layer, enabling emission at 6 V under a curved state. Combining standard OLED stacks (TPD/Alq3/LiF/Al) with plant-derived CDP guides eco-friendly and energy-conscious device design.
Why it matters / Key points
- CDP inclusion/porosity mitigates aggregation and optimizes interfacial recombination.
- Alq3-based green emission (λmax ≈ 520 nm) with up to 19,620 cd m−2 luminance.
- Emission observed at 6 V even when bent, suggesting flexibility potential.
- Simple insertion of CDP into a conventional ITO/TPD/Alq3/LiF/Al stack.
- Plant-derived CDP supports environmentally conscious device engineering.
Highlights by study
- Design/Materials: Vacuum-deposited five-layer OLED: ITO / TPD / CDP (α, β, γ) / Alq3 / LiF / Al.
- Function/Phenomena: CDP pores reduce self-association and nonradiative quenching at interfaces.
- Performance: Max luminance 19,620 cd m−2; green emission at 6 V in a curved state.
- Use cases: Energy-saving displays/lighting, flexible surfaces, eco-friendly photonic devices.
Mini-glossary
- CDP (Cyclodextrin Polymer): Crosslinked, porous network of CDs for inclusion and interfacial control.
- Interlayer: Layer inserted to modulate charge injection/recombination and suppress quenching.
- TPD: A common hole-transport material in OLEDs.
- Alq3: Green-emitting tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium.
- ITO: Transparent conducting oxide electrode (indium tin oxide).
Potential applications
- Energy-efficient displays and lighting (lower-voltage operation)
- Flexible/curved OLEDs (stable emission under bending)
- Green electronics using plant-derived materials
- Teaching/demonstration kits for organic electronics
Suggested tags
#Cyclodextrin #CDP #OLED #Interlayer #Alq3 #TPD #ITO #GreenEmission #EnergySaving #FlexibleDevice
参考文献 / References
- Hara, M.; Umeda, T.; Kurata, H. Fabrication and Characterisation of Organic EL Devices in the Presence of Cyclodextrin as an Interlayer. Sensors 2021, 21(11), 3666. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113666
powered by ChatGPT